Benefits and Properties of Lion's Mane
Lion's Mane: A natural treasure for your mind and body
What if you could improve your memory and protect your brain with a natural ingredient? It's not science fiction. It's Hericium erinaceus, an ancient mushroom with an unmistakable appearance that resembles a lion's mane.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, it has been revered for centuries as a tonic to strengthen energy and mind. Today, modern science is confirming this ancestral wisdom, revealing why this mushroom is considered an essential superfood. In this article, you'll discover its benefits and the science behind its incredible properties.

The science behind Lion's Mane: bioactive compounds
While Lion's Mane possesses a valuable nutritional profile, its true power lies in two groups of unique compounds that make it a top-tier nootropic mushroom. These are hericenones and erinacines.
Hericenones: nerve growth activator
Hericenones are found mainly in the mushroom's fruiting body (the visible part that is consumed). Their main function is to stimulate the production of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF). NGF is a crucial protein for brain health, acting as a "fertilizer" for neurons, helping them grow, stay healthy, and establish new connections. By enhancing NGF synthesis, hericenones contribute directly to neurogenesis, a vital process for memory, learning, and preventing cognitive decline.
Erinacines: neuroprotective shield
On the other hand, erinacines are found in the mycelium (the network of hyphae or "roots" of the mushroom). These potent molecules are the subject of intense research for their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and exert a direct neuroprotective effect. Erinacines not only protect neurons from damage, but also promote brain plasticity, allowing the brain to reorganize and form new neural pathways. This dual effect of protection and regeneration makes them a promising field in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
| Compound | Location | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hericenones | Mushroom body (visible part) | Stimulate Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), key for neuronal regeneration. |
| Erinacines | Mycelium (underground network) | Offer a potent neuroprotective effect and improve brain plasticity. |
The importance of hericenones + erinacines synergy
When we talk about neuroprotection, it's not enough to stimulate the growth of new neurons or protect existing ones: both functions must coexist for a real and lasting effect. This is where Lion's Mane makes the difference compared to other natural nootropics.
Hericenones, present in the fruiting body, act as "builders," driving NGF production and favoring neurogenesis (creation of new neurons). Meanwhile, erinacines, concentrated in the mycelium, function as "guardians": they cross the blood-brain barrier to protect neurons from oxidative damage and inflammation, while enhancing brain plasticity.
Together, these compounds allow the brain to not only maintain its vitality with age, but also be better prepared to learn new things, recover from stress, and resist cognitive decline. This duality—construction + protection—is the distinctive hallmark that makes Lion's Mane a unique ally for long-term mental health.
Lion's Mane health benefits
Nervous system health and cognition
One of the fields where Lion's Mane has awakened the greatest scientific interest is in its relationship with brain health. Traditionally used as a mind tonic in Asian medicine, modern studies confirm this reputation.
In animal models, supplementation with Hericium erinaceus has demonstrated the ability to reverse memory impairment associated with aging and enhance learning in young and healthy individuals. These effects are related to erinacines and hericenones, which favor neurotransmission in key areas like the hippocampus.
Neuroprotective effects are also described. In animal models of Alzheimer's, the extracts reduced amyloid plaque accumulation and stimulated neurogenesis, that is, the formation of new neurons in the hippocampus and cerebellum, suggesting a dual potential: prevention of deterioration and support for the regeneration of damaged neural circuits.
However, most of the evidence comes from animal or laboratory studies. Studies in humans, although promising, remain preliminary; therefore, effects on memory, concentration, and protection should be understood as an area in full scientific exploration.
Neuroprotection and emotional wellbeing: two sides of the same coin
We often think of memory and mood as separate areas, but in reality they are deeply connected. Chronic inflammation and loss of neuronal plasticity not only affect cognition, but are also associated with increased risk of anxiety and depression.
By stimulating neuronal growth and reducing inflammatory processes, Lion's Mane compounds create more fertile ground not only for memory and learning, but also for a more stable emotional balance. In other words, supporting brain health with this mushroom simultaneously means strengthening emotional resilience against stress and promoting a more positive mood.
Digestive system support
Hericium erinaceus has been used to protect the stomach and promote easier digestion. Recent research suggests that its regular consumption helps maintain better balance in the intestinal flora, as an increase in beneficial bacteria and a reduction in harmful ones has been observed.
Its effect on intestinal mucosa protection has also been studied. In animal models, the mushroom's compounds have demonstrated their ability to calm inflammation and promote recovery of damaged tissues. This suggests a possible supportive role in situations where the intestine needs extra reinforcement, acting comprehensively on the mucosa, inflammation, and microbiome.
Immune system strengthening
Lion's Mane also stands out for its ability to support the immune system. Its polysaccharides have shown a clear immunomodulatory effect. In laboratory studies, they can stimulate the production of certain signaling molecules—like cytokines—that help activate the body's defensive response.
These polysaccharides also strengthen key immunity organs, such as the thymus and spleen, and improve antioxidant activity. Additionally, they contribute to the proliferation of defensive cells, increase the action of macrophages and NK cells (natural killer), and even support intestinal immunity through different cellular pathways.
Mental and emotional wellbeing
In addition to its effects on the brain and immune system, Lion's Mane could positively influence our emotional state. In a small study with 30 women, it was observed that after four weeks of consumption, symptoms of anxiety and mild depression decreased notably.
These results suggest that this mushroom could act as a natural ally to modulate stress and promote a more balanced mood. However, it's important to highlight that these are initial studies of reduced size. To confirm these effects, broader and more rigorous research is needed.
Cardiovascular benefits
Some initial studies suggest that Lion's Mane could contribute to cardiovascular health. In animal models, it has been observed that extracts from this mushroom can help reduce triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels. Certain bioactive compounds also seem to influence blood pressure regulation, thanks to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity. However, available evidence remains incipient and comes largely from animal research, so much more clinical research in humans is required.
Lion's Mane is much more than a curious-looking mushroom: its value lies in the unique synergy of hericenones and erinacines, which give it a remarkable capacity to support brain function and nervous system health in the long term. Thus, this ancient remedy becomes a superfood that combines ancestral wisdom with modern science validation, offering an exceptional ally for our integral wellbeing.
Nutritional profile of Hericium Erinaceus
Lion's Mane is a nutritional treasure. It's rich in proteins, ideal for vegetarian diets, and contains essential amino acids, B-group vitamins, and important minerals like zinc, potassium, and iron. The dietary fiber it provides is essential for digestive health and for a prolonged feeling of satiety.
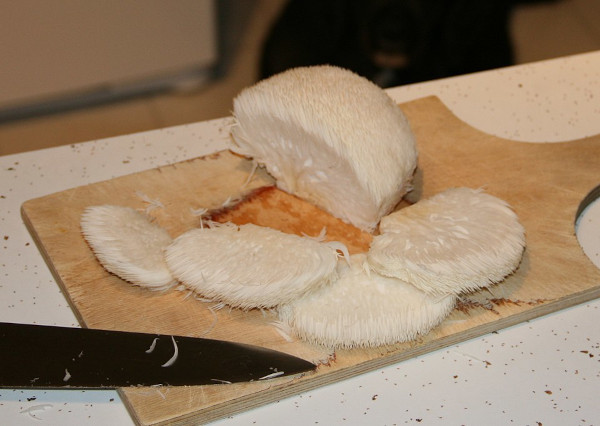

Lion's Mane is a versatile mushroom that can be enjoyed both in cooking and in supplement form. Its growing popularity is due not only to its healthy properties, but also to the variety of ways it can be integrated into daily life.
Culinary consumption
In its fresh version, Lion's Mane is considered a gourmet ingredient. Its meaty texture and delicate flavor, with notes reminiscent of seafood (crab or lobster), make it a culinary gem highly appreciated by chefs and healthy cooking enthusiasts. It can be sautéed, grilled, added to stews, or even used as a vegetable substitute for meat or fish.
Supplementation
When the goal is to maximize its bioactive compounds, supplementation offers practical and concentrated options:
- Capsules and powders: These are the most common form of consumption, convenient for incorporating into daily wellness routines.
- Liquid extracts: They have the advantage of faster absorption and allow easy dosing of a few drops per day.
The key difference: fruiting body extract + mycelium
Not all supplements are equal. The highest quality ones combine fruiting body extract (where hericenones are found) and mycelium (rich in erinacines). This synergy ensures the presence of both star compounds and maximizes the neuroprotective and regenerative benefits of the mushroom.
Considerations and precautions
Lion's Mane is a mushroom considered safe for most people. However, it's important to consider some factors:
-
Possible adverse effects: Although infrequent, some people sensitive to mushrooms may experience mild allergic reactions, such as digestive discomfort or skin irritations. If it's your first time consuming it, it's advisable to start with a reduced amount.
-
Drug interactions: It's recommended to always consult with a healthcare professional before taking Lion's Mane in supplement form if you're under treatment with anticoagulants or immunosuppressants.
-
The importance of quality: Choosing supplements from reliable sources, with traceability and certifications ensures they actually contain the active compounds and are free from contaminants.
Lion's Mane is much more than a curious-looking mushroom: it represents a bridge between ancestral wisdom and modern science discoveries. Its nutritional richness, together with the presence of unique compounds like hericenones and erinacines, makes it a promising ally for brain care, digestive health, immune system, and integral wellbeing.
Although studies remain to be conducted to understand its full therapeutic scope, the truth is that this ancient mushroom is gaining a prominent place in contemporary research and healthy cooking. Incorporating it into our lives is also an invitation to reconnect with nature and recognize that, sometimes, the best treasures for our health have always been around us, waiting to be rediscovered.
Whether in cooking or in quality supplements, integrating Lion's Mane into daily routine is a small gesture with great potential for your future health.
Relevant scientific studies
This section provides rigorous scientific support for the benefits described in the text.
-
Memory and concentration improvement
Studies in mice have demonstrated that supplementation with Hericium erinaceus can reverse recognition memory impairment associated with aging, through extracts containing erinacines A and hericenones C and D. [1] Another study in healthy mice showed that the mushroom improves recognition memory and increases neurotransmission in mossy fiber–CA3 synapses in the hippocampus, a key area for memory. [2]
Stimulation of nerve growth factor (NGF) is one of the most relevant mechanisms: fruiting body extracts induce an increase in NGF expression in human cells. -
Neuroprotective protection
In animal models, it has been observed that administration of extractions with erinacines and hericenones can reduce amyloid plaque burden (typical of Alzheimer's) and promote neurogenesis in the hippocampus and cerebellum. [3]
Although results are promising, we emphasize that human studies are still in preliminary phases. -
Anti-inflammatory action and gut microbiota support
In clinical studies, its consumption has shown the ability to improve microbiome diversity, increasing beneficial bacteria and reducing pathogenic strains. [4]
Additionally, in animal models (primates with spontaneous ulcerative colitis), polysaccharides from H. erinaceus mycelium attenuate symptoms, restore intestinal health, and favorably modulate the microbiota. [5] Studies in immunosuppressed mice have also identified that these polysaccharides protect the intestinal barrier and increase antioxidant enzymes like GSH-PX and SOD, reinforcing key intercellular junction proteins. [6] -
Immunomodulatory effect
In experiments with macrophages, polysaccharides extracted from the mushroom enhanced the production of cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α. In mice, they improved thymus and spleen structure, as well as levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, and antioxidant activity. [7]
Other studies detail that these polysaccharides also stimulate lymphocyte proliferation, NK and macrophage activity, and activation of cellular pathways like MAPK and AKT in intestinal immunity. [8] -
Antioxidant action
It has been demonstrated that H. erinaceus polysaccharides have outstanding capacity to neutralize free radicals. Additionally, in D-galactose-induced aging models in mice, modified versions of these polysaccharides reduced oxidative stress and protected both liver and brain. [9] -
Stress and anxiety reduction
In a small pilot study, a decrease in anxiety and mild depression symptoms was observed after 4 weeks of H. erinaceus consumption. [10] -
Lipid profile improvement and cardiovascular protection
Studies in rodents with high-fat diets have shown significant reduction in triglyceride, total cholesterol (TC), and LDL levels, along with HDL increase. [11] In vitro assays indicate that mushroom fractions can inhibit LDL oxidation. [12] A 2025 study demonstrated that an Hericium erinaceus protein (HEP) in obese mice improved insulin resistance and fatty acid oxidation. [13] A recent review mentions that this mushroom possesses compounds that could act on disorders like obesity and hypertension. [14]
Bibliographic sources
- [1, 3] Ratto, Daniela et al. "Hericium erinaceus Improves Recognition Memory and Induces Hippocampal and Cerebellar Neurogenesis in Frail Mice during Aging." Nutrients vol. 11,4 715. 27 Mar. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11040715
- [2] Brandalise, Federico et al. "Dietary Supplementation of Hericium erinaceus Increases Mossy Fiber-CA3 Hippocampal Neurotransmission and Recognition Memory in Wild-Type Mice." Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM vol. 2017: 3864340. doi:10.1155/2017/3864340
- [4] Gravina, Antonietta Gerarda et al. "Hericium erinaceus, a medicinal fungus with a centuries-old history: Evidence in gastrointestinal diseases." World journal of gastroenterology vol. 29,20 (2023): 3048-3065. doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3048
- [5] Ren, Zhengyu et al. "Hericium erinaceus mycelium-Derived Polysaccharide Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Cynomolgus Monkeys." Molecular nutrition & food research vol. 67,3 (2023): e2200450. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202200450 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36443636/
- [6] Tian, Baoming et al. "Ameliorating effects of Hericium erinaceus polysaccharides on intestinal barrier injury in immunocompromised mice induced by cyclophosphamide." Food & function vol. 14,6 2921-2932. 20 Mar. 2023, doi:10.1039/d2fo03769f
- [7] Han, Yujiao et al. "Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide improves the microstructure, immune function, proliferation and reduces apoptosis of thymus and spleen tissue cells of immunosuppressed mice." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry vol. 87,3 (2023): 279-289. doi:10.1093/bbb/zbac198
- [8] Yang Y, Li J, Hong Q, Zhang X, Liu Z, Zhang T. Polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus Fruiting Bodies: Structural Characterization, Immunomodulatory Activity and Mechanism. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3721. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183721
- [9] Li H, Zhao H, Liu W, Feng Y, Zhang Y. Liver and brain protective effect of sulfated polysaccharides from residue of lion's mane medicinal mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes), on D-galactose−induced aging mice. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2021;23(5):55-65. doi:10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2021038241
- [10] Brandalise, Federico et al. "Dietary Supplementation of Hericium erinaceus Increases Mossy Fiber-CA3 Hippocampal Neurotransmission and Recognition Memory in Wild-Type Mice." Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM vol. 2017 (2017): 3864340. doi:10.1155/2017/3864340
- [11] Hiwatashi, Kazuyuki et al. "Yamabushitake mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) improved lipid metabolism in mice fed a high-fat diet." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry vol. 74,7 (2010): 1447-51. doi:10.1271/bbb.100130
- [12] Rahman, Mohammad Azizur et al. "Inhibitory effect on in vitro LDL oxidation and HMG Co-A reductase activity of the liquid-liquid partitioned fractions of Hericium erinaceus. BioMed research international vol. 2014 (2014): 828149. doi:10.1155/2014/828149
- [13] Lu H, Yang S, Li W, Zheng B, Zeng S, Chen H. Hericium erinaceus Protein Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress In Vivo. Foods. 2025; 14(3):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030459
- [14] Banerjee, Sabyasachi, et al. "Unlocking the Potential of Lion's Mane Mushroom (Hericium erinaceus)." Journal of Applied and Natural Science, vol. 16, no. 1, 20 Mar. 2024, doi:10.31018/jans.v16i1.5224.
Related posts
-
The life cycle of fungi
Published : 2025-04-29 14:38:10 -
Fusarium venenatum, the fungus challenging the meat industry's efficiency
Published : 2025-12-12 15:28:57 -
Yarsagumba: Fever for the costliest fungus devouring the Himalayas
Published : 2025-12-18 21:50:15



























I try to order Dowels for lion manes 200 pc but I dont get to the payment page.
View replies (1) -
Hi Henri, We’re currently working on getting our online store ready so we can start offering our products directly. For this reason, the shopping cart is temporarily disabled. In the meantime, you can purchase dowels through our friends at Boscum here: https://boscum.com/en/lions-mane-plug-spawn-15.html We also invite you to subscribe to our newsletter — we’ll let you know as soon as orders are available on our website. Best regards, Mushverse Team